
In this type of questions, we are asked to find the number of networks and host addresses in each network from a given address space. Finding the number of networks and host addresses in each network

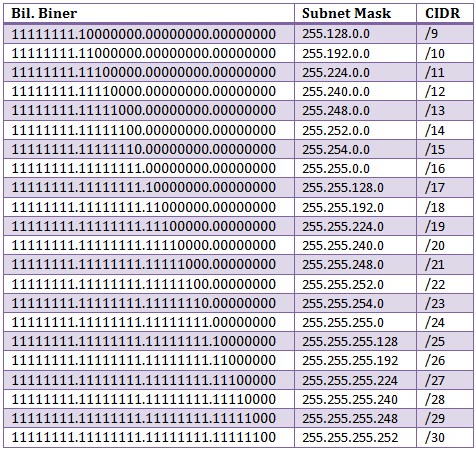
Let’s understand the each type of Subnetting question in detail with examples. Find the type of given address, network ID and broadcast ID.Find the number of networks and number of host addresses in each network.Subnetting QuestionsĪ Subnetting question can be asked in three ways. Besides these two addresses, all remaining addresses are considered as valid host addresses. In each network first address and last address are always reserved for network address and broadcast address respectively. We can create 8 networks from 3 Subnetting host bits. To know how many Subnetting bits are required to create how many networks, we use power of 2.įor example if we want to know many networks can be created from 3 Subnetting bits, we will use power 2 three times. Subnetting can be done only in Subnetting eligible host bits. If we exclude reserved network bits and host bits from total IP bits, we will get Subnetting eligible host bits. In all three classes last 2 bits are reserved for host addresses. In class A, B and C first 8, 16 and 24 bits are reserved for network address respectively. Subnetting cannot be done in class D and E. From these, only first three classes A, B and C are used in Subnetting. There are five IP classes A, B, C, D and E. In Subnetting questions, mostly second type is used. Following table lists some examples of both types. In abbreviated form only the number of network bits are written along with IP address.
Subnet mask table class a full#
In full form a decimal value of each octet is written along with IP address. Octets are separated by periods and written in a sequence.Ī Subnet mask can be written in two ways in full form and in abbreviated form. Without subnet mask an IP address is an ambiguous address and vice versa.īoth IP address and Subnet mask consists 32 bits. While reading an IP address how much portion should be treated as network address and how much portion should be treated as host address is decided by an another address known as Subnet mask.Īn IP address is always used with Subnet mask. Network address is always written first in sequence. Key points of Subnettingīefore we start working with Subnetting examples, let’s have a quick recap of important Subnetting concepts and terms from previous parts of this tutorial.Īn IP address is the combination of two addresses network address and host address. It explains Supernetting in detail with examples.

This tutorial is the last part of the article.
Supernetting Tutorial: - Supernetting Explained with Examples

It explains VLSM Subnetting examples for Cisco exams and interviews. This tutorial is the sixth part of the article. VLSM Subnetting Examples and Calculation Explained It explains what VLSM Subnetting is and how it is done step by step including differences between FLSM Subnetting and VLSM Subnetting. This tutorial is the fifth part of the article. It explains the Subnetting concepts and terms such as network id, broadcast id, total hosts, valid hosts, power of 2, block size and CIDR in detail. This tutorial is the third part of the article. Subnetting Tutorial - Subnetting Explained with Examples It explains what Subnetting is and why it is necessary in computer network along with the advantages of Subnetting. This tutorial is the second part of the article. It explains IP addressing and network addressing such as IP address, subnet mask, IP address types and IP classes in detail.īasic Subnetting in Computer Networks Explained This tutorial is the first part of the article. Network Address Broadcast Address and IP Address Explained Other parts of this article are following. This tutorial is the fourth part of the article “ IP Subnetting in Computer Network Step by Step Explained with Examples”.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
